Metals or thermoplastics can be joined together by a process called laser welding, which uses a laser beam to create a weld. As a concentrated heat source, laser welding can generate narrow, deep welds between square-edged pieces in thicker materials and high welding speeds of meters per minute in thin materials. Read More…
At Edge Metalworks, we pride ourselves on providing top-notch laser cutting services to our valued customers. Our team is equipped with state-of-the-art laser cutting technologies that range from 4kw – 24kw and enable us to precisely cut a wide variety of metals and thicknesses, catering to the unique specifications of each project. Our commitment to quality ensures that our products meet the...
Great Lakes Engineering is a trend setting manufacturer of surface mount stencils, precision laser cut parts, and photo chemical etched parts. We work with a wide range of materials, including Stainless Steel, Copper, Brass, Titanium, Nitinol, Nickel, Kovar and many others.

Our teams at Remaly Manufacturing Company, Inc. utilize state of the art equipment to provide you with laser cutting capabilities. Our teams provide cutting services for a wide range of materials such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel, monel and much more.
Our fiber optic metal laser cutting capabilities include Stainless steel, Aluminum, CRS and other ferrous and nonferrous metals. We can laser cut flat blanks, stencils, signs, prototypes, and custom formed fabricated parts.

Sharpe Products specializes in custom pipe and tube bending and tube laser cutting. With three powerful, 4kW laser cutting systems, and a robotic, multi-axis 3 kW laser cutting system, we cut round, square, rectangle and open profiles, up to 6-inch OD. Typical cutouts include angles, copes, notches, perforations, slots, or other custom hole patterns, either before or after tube bending. We...
Our laser cutting services are used by leading manufacturers. We have a 10k square foot laser production facility with cutting capabilities up to .625” on steel which processes material quickly. Stocking much carbon steel allows us to pass along the savings. We serve automotive & trucking industries.

More Laser Welding Companies
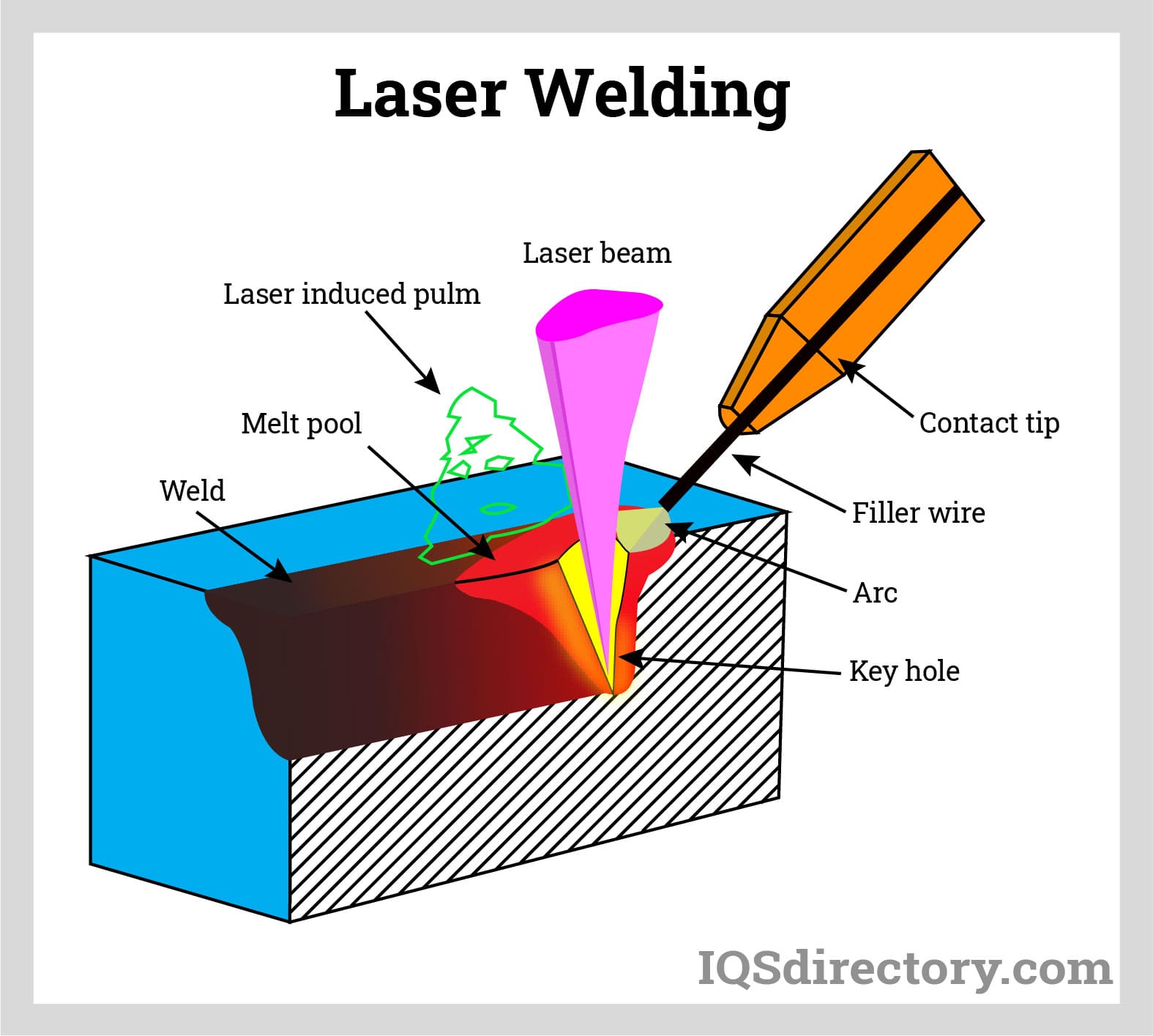
Modes of Laser Welding
The two fundamentally different ways laser welding works are conduction-restricted and keyhole welding. The power density of the laser beam that strikes the workpiece will determine how it interacts with the welding material.
Conduction-limited welding occurs when the power density is less than 105W/cm2. As a result, the laser beam does not penetrate the material; it is absorbed into its surface. Due to this, conduction-constrained welds frequently have a large width-to-- depth ratio.
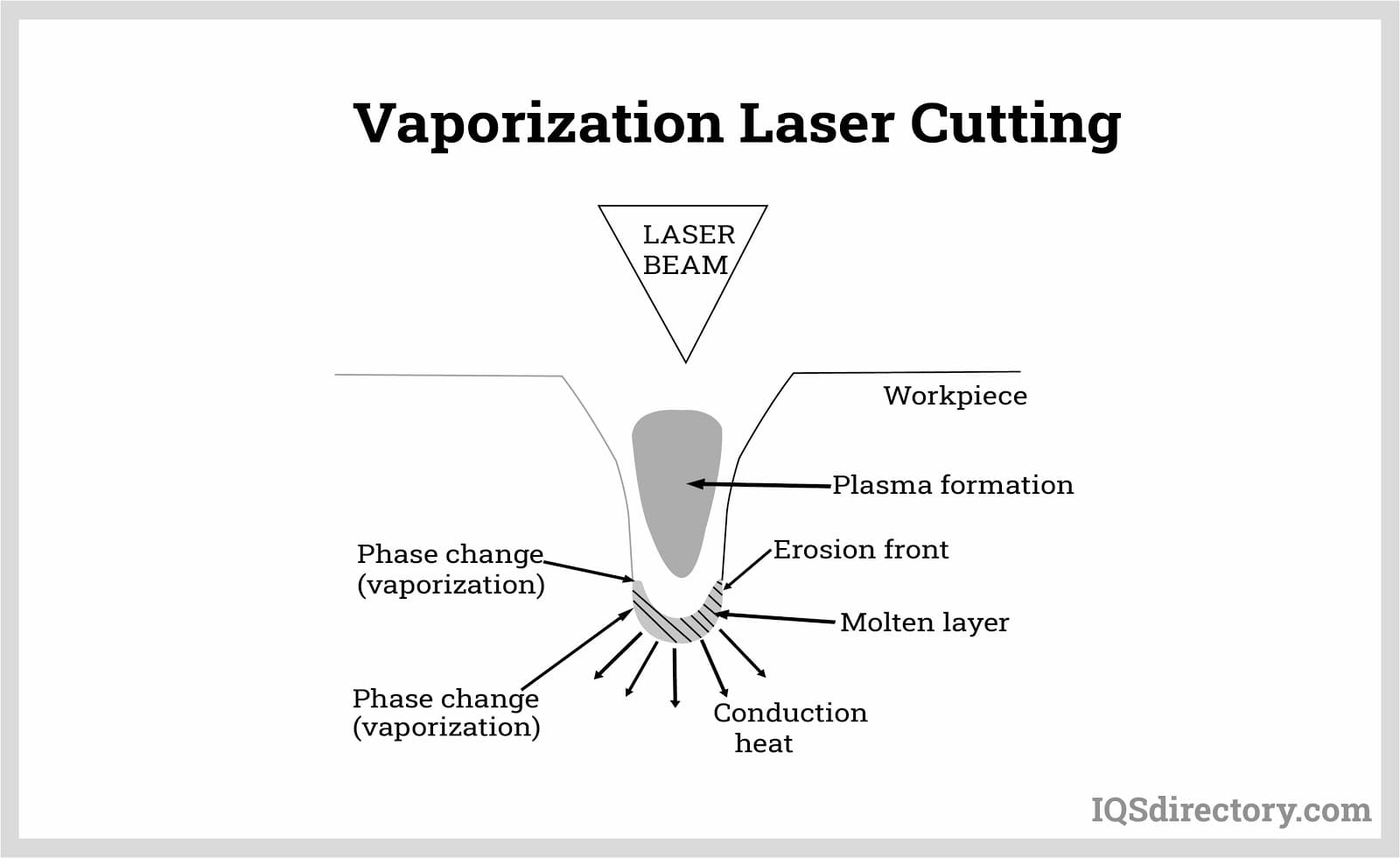
Higher power densities and a keyhole mechanism are increasingly frequently used to perform laser welding. Before a sizable amount of heat can be dissipated by conduction, the material in the path of the laser beam melts and evaporates when the laser beam is focussed to a small enough spot to create a power density typically > 106-107 W/cm2. Once inside the workpiece, the concentrated laser beam creates a "keyhole" chamber filled with metal vapor (which, in some cases, can even be ionized, forming plasma). The molten walls of the keyhole in this cavity are kept from collapsing by the increasing vapor or plasma.
Additionally, the creation of this keyhole significantly enhances the coupling of the laser beam with the workpiece. The joint is then moved in relation to the laser beam or traversed along the joint to be welded to accomplish deep penetration welding. Welds with a high depth-to-width ratio are the outcome of this. Due to surface tension, a part of the molten material at the keyhole's leading edge flows around the keyhole cavity to the back, cools, and solidifies to form the weld. As a result, the weld cap now has a chevron pattern that points rearward toward the weld's origin.
The Process of Laser Welding
Laser welding produces a very small, extremely concentrated point of light absorbed by the surrounding material, which then becomes very energetic. With the use of strong laser beams, the electrons in the region become agitated to the point that the material melts due to the atoms rupturing their bonds with one another.
Plastics can also be joined with laser welding, and melting the two materials at their seams creates a junction. It is amazing how powerful light can be to melt metal within milliseconds. The laser welding equipment uses several elements that guide and amplify the laser to produce such strong laser beams.
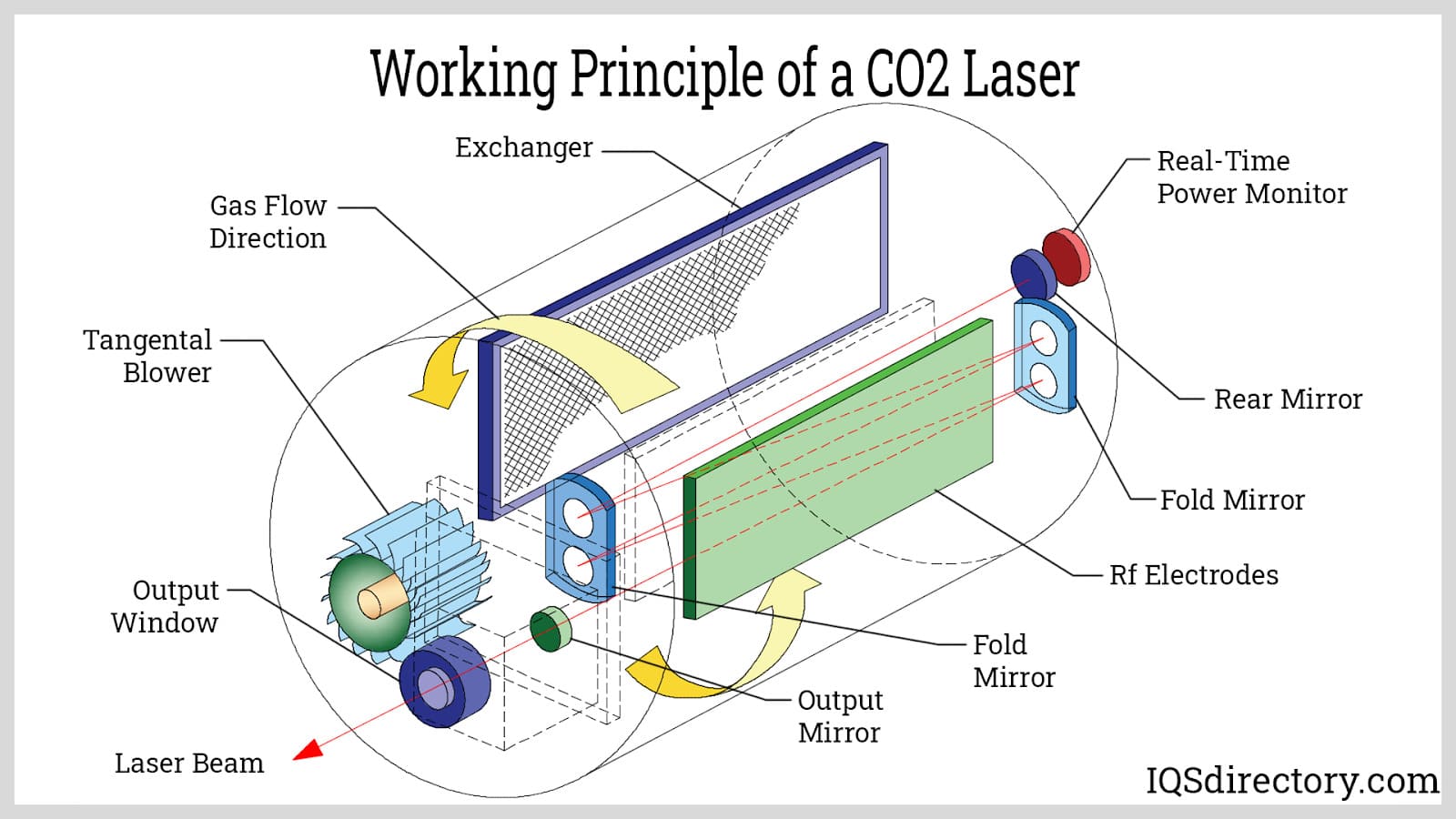
Typically, optical fibers provide the laser beam to the laser welding machine. There are machines for welding single fibers and machinery for welding numerous fibers. Each fiber in the multiple fiber welding equipment is connected to a laser, and as more fibers are added, the laser's power grows. A collimator and focusing lens are frequently used to focus the beam before it leaves the machine.
To generate a hybrid laser arc welding, laser welding is frequently combined with arc welding. Any arc welding method, such as MIG, TIG, or SAW, is combined with deep penetration laser welding in hybrid laser arc welding. The result is a weld that benefits from both types of welding. The resulting weld will have deep penetrating joints and increased joint fit-up tolerance. Additionally, unfavorable outcomes like cracking and internal porosity are diminished.
Types of Laser Welds
Laser welding primarily employs the butt, overlap, fillet, lap, and edge flange weld geometries. Each has characteristics that fit particular uses. We examine a few of these categories below.
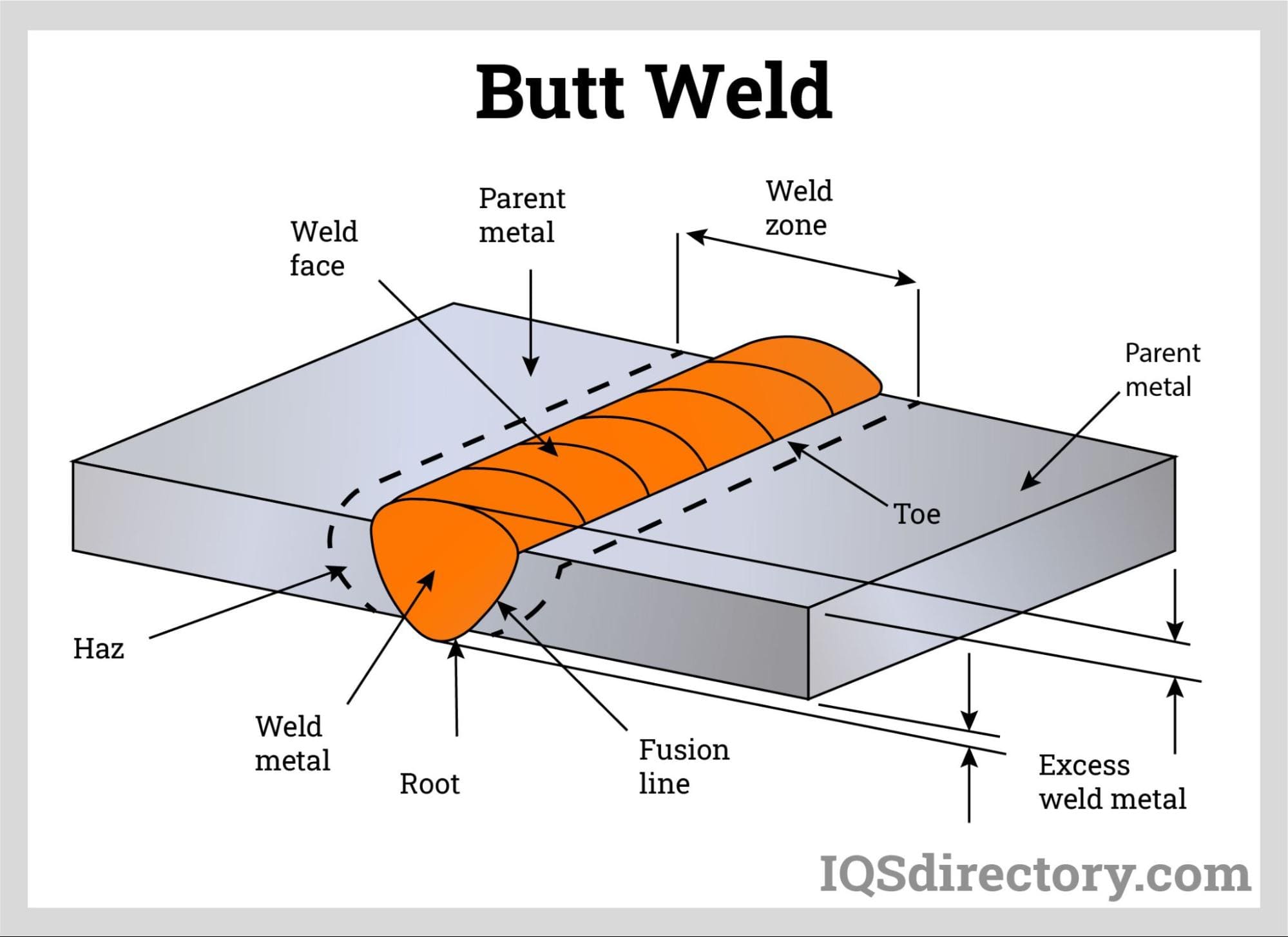
Butt Weld
The butt weld is the least forgiving for part fit-up and the minimum part thickness restriction and is most effective for laser power vs. weld strength & speed. The weld strength is directly connected to weld depth.
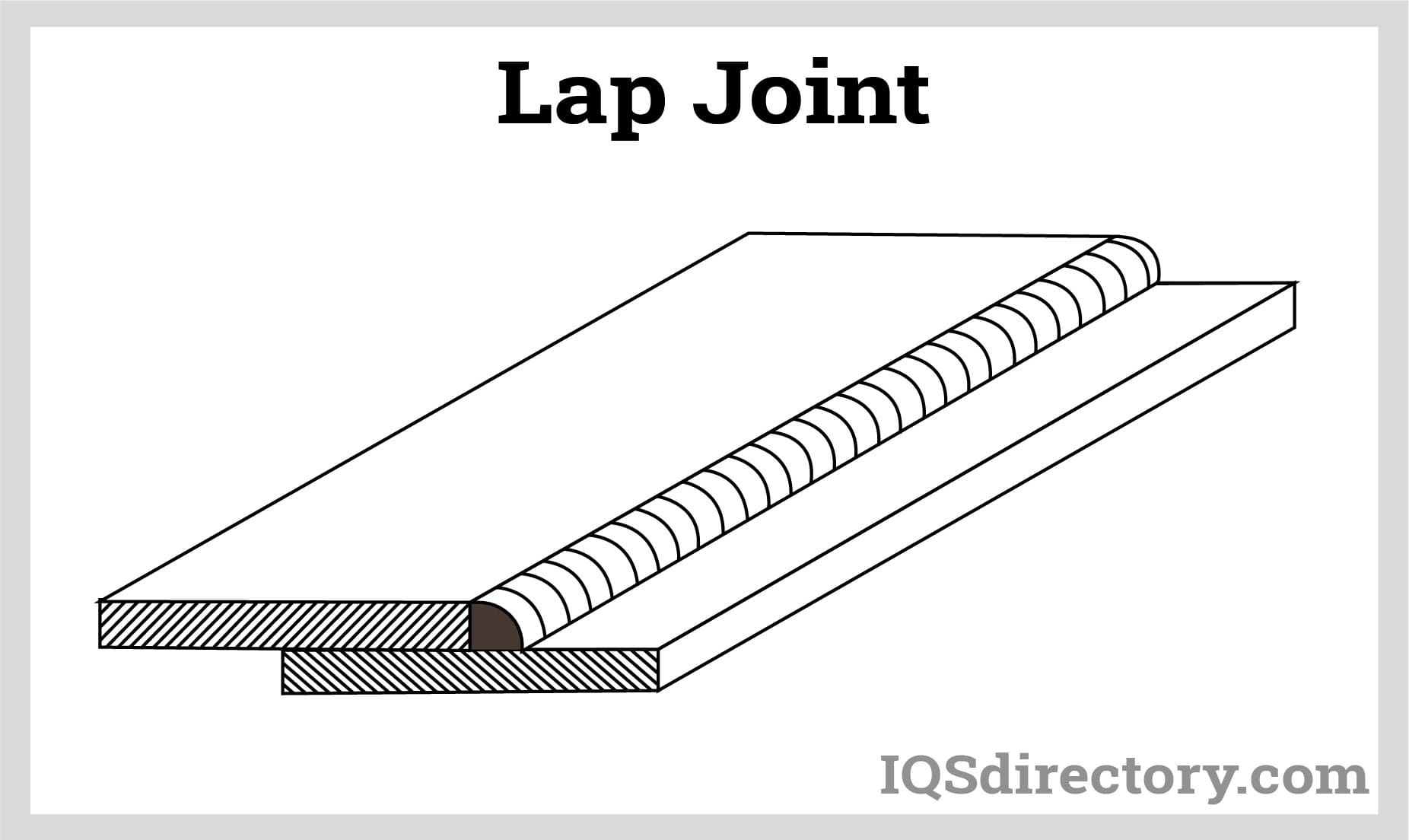
Lap Weld
The lap weld is the most accommodating for component fit-up since it has weld strength from the weld width at the interface and prefers thin (top) to thick materials.
Fillet Weld
The laser gets stronger, forgiving for fit-up, and may need a more complex design or motion if it is angled toward the workpiece. However, if the laser is pointed at the workpiece, it becomes easier to configure and limit the thickness of the top component to 0.02′′.
Using a gas, solid, or liquid as a medium will allow laser beams to be extracted—using a gas or solid as the medium occurs most frequently with welding lasers. So, solid-state or gas lasers can generalize the lasers used for laser welding. For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) or other gases create light during gas laser welding. To produce light, solid-state laser welding (such as YAG laser welding) needs ores like yttrium, aluminum, and garnet.
Advantages of Laser Welding
When compared to traditional welding methods, laser welding has the following advantages:
- Laser welding is a quick and productive method; it is eight times faster than TIG welding and about twice as fast as plasma welding.
- Laser welding results in little distortion and a small heat-affected zone.
- The laser welding method is quiet and hygienic.
- With laser welding, great dimensional tolerances are possible.
- Laser welding is the best option for joining materials that only tolerate a small amount of heat.
- Laser welding is frequently used to join disparate and challenging-to-weld materials.
Disadvantages of Laser Welding
- The rapid cooling rate can locally harden hardened steel; laser welding produces a low width depth ratio weld that may cause thermal cracking; and the equipment investment cost is relatively high.
- Laser welding machines use a lot of energy and are not appropriate for joining thick metals.
- Health risks related to laser welding machines must be considered and eliminated.
Choosing the Right Laser Welding Company
To ensure you have the most beneficial outcome when selecting a laser welding company, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of laser welding companies. Each laser welding company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the business for more information or request a quote. Review each laser welding company website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple laser welding businesses with the same form.






 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services