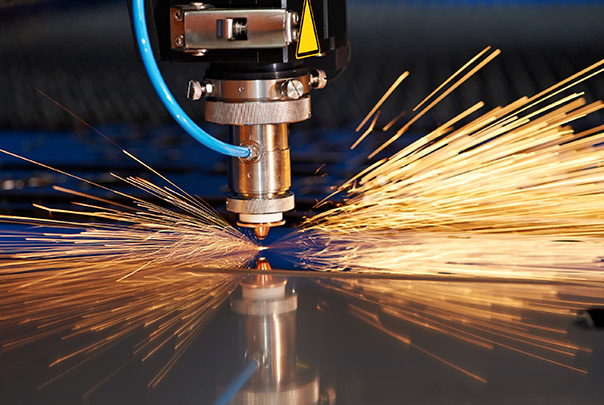
Laser cutting is a hot cutting process used to cut materials like metal or sheet metal. Laser cutter Service providers generally employ a carbon dioxide laser to perform the low-distortion hot cutting. The “cut” of a laser is actually an energy transfer that causes the material to melt or burn along a line. Read More…
At Edge Metalworks, we pride ourselves on providing top-notch laser cutting services to our valued customers. Our team is equipped with state-of-the-art laser cutting technologies that range from 4kw – 24kw and enable us to precisely cut a wide variety of metals and thicknesses, catering to the unique specifications of each project. Our commitment to quality ensures that our products meet the...
Great Lakes Engineering is a trend setting manufacturer of surface mount stencils, precision laser cut parts, and photo chemical etched parts. We work with a wide range of materials, including Stainless Steel, Copper, Brass, Titanium, Nitinol, Nickel, Kovar and many others.

Our teams at Remaly Manufacturing Company, Inc. utilize state of the art equipment to provide you with laser cutting capabilities. Our teams provide cutting services for a wide range of materials such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel, monel and much more.
Our fiber optic metal laser cutting capabilities include Stainless steel, Aluminum, CRS and other ferrous and nonferrous metals. We can laser cut flat blanks, stencils, signs, prototypes, and custom formed fabricated parts.

Sharpe Products specializes in custom pipe and tube bending and tube laser cutting. With three powerful, 4kW laser cutting systems, and a robotic, multi-axis 3 kW laser cutting system, we cut round, square, rectangle and open profiles, up to 6-inch OD. Typical cutouts include angles, copes, notches, perforations, slots, or other custom hole patterns, either before or after tube bending. We...
Our laser cutting services are used by leading manufacturers. We have a 10k square foot laser production facility with cutting capabilities up to .625” on steel which processes material quickly. Stocking much carbon steel allows us to pass along the savings. We serve automotive & trucking industries.

More Laser Cutting Company
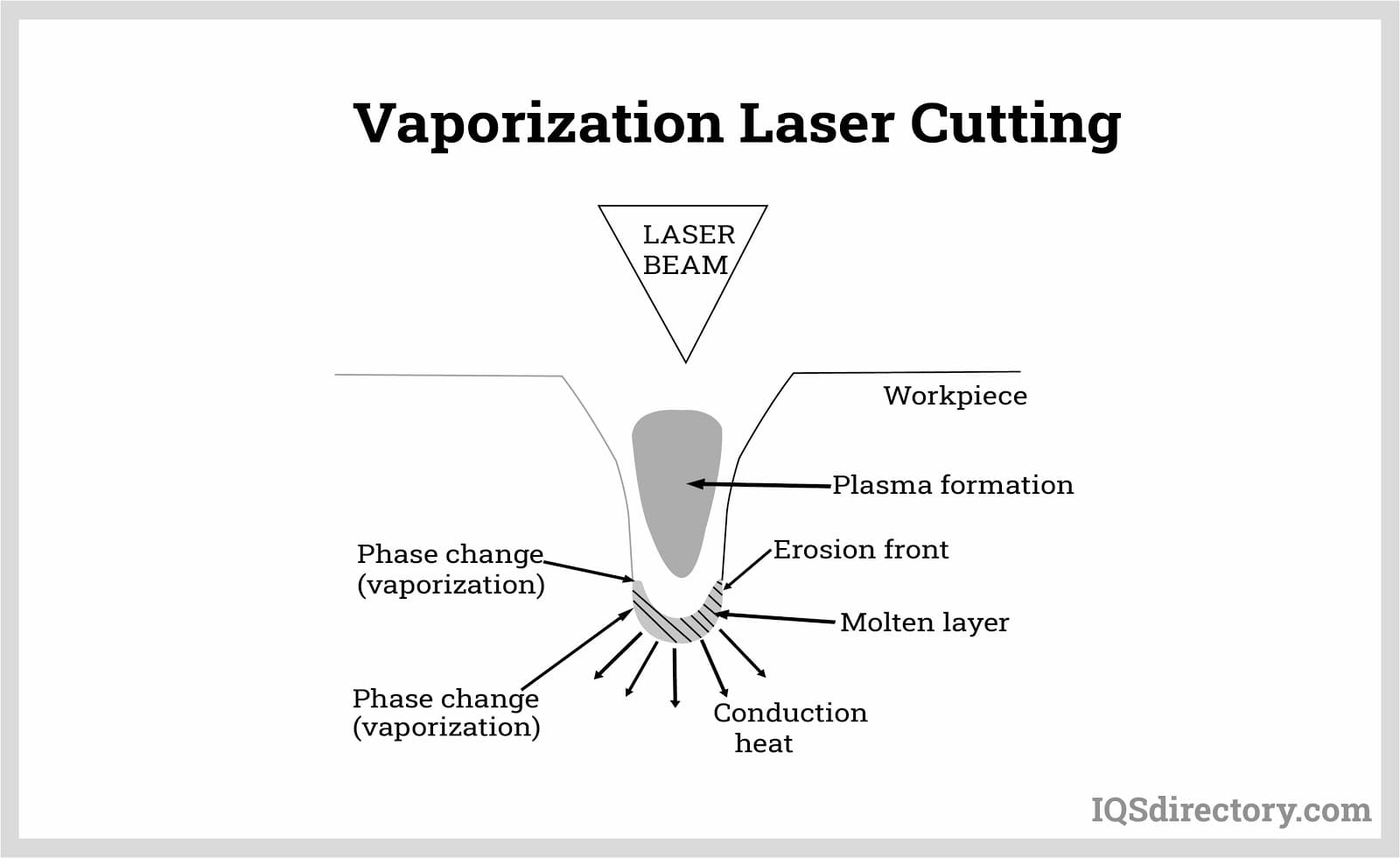
The term “laser” is an acronym for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation,” and a laser beam is a highly focused wavelength radiation that remains concentrated without dispersing. Laser cutting offers precision on a smaller scale, surpassing any other metal cutting method in accuracy.
Laser Cutting Applications
Lasers, with their ability to cut, slice, vaporize, and melt, also offer a range of machining and micromachining services such as drilling, welding, etching, and engraving. This remarkable technology is vital across many industries, particularly those demanding microscopic tolerances and precise accuracy, like microtechnology and electronics. Additionally, lasers find applications in HVAC, medical devices, communications, automotive manufacturing, plumbing, and military and defense sectors.
Products Produced from Laser Cutting Services
Aerospace and automotive manufacturing industries use laser cutting to fabricate pieces like precision parts, gaskets, solar cells, nozzles, and circuit boards. Cell phone parts, transducers, microchips, and military and communication devices rely on laser cutting as well. Even water piping and refrigeration systems have some laser cut elements. In the medical industry, laser cutting is used to drill hypo-tubes, catheter holes, filtering devices, gas flow orifices and other highly intricate devices.
Laser Cutting History
Laser cutting technology emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in the mid-20th century. Although Albert Einstein theorized laser technology in the early 1900s, it wasn’t until 1960 that engineers brought the first laser to life. This pioneering device, a solid-state pink ruby laser, was crafted by American engineer and physicist Theodore H. Mainman. Fast forward four years, and engineer Kumal Patel in New Jersey introduced the first gas laser cutter, utilizing CO2, marking another significant milestone in laser technology.
Just one year later, engineers at Western Electric Engineering Research Center produced the first-ever metal-cutting laser. They used this groundbreaking technology to drill holes into diamond dies. In a New York Times article titled “New Work Found for Lasers at Western Electric,” William Freeman described the laser as a beam of light so intense it could penetrate far into space carrying a voice, cut metal like a power saw cuts lumber, and burn holes in diamonds, quickly becoming an industrial workhorse.
In 1967, British engineers introduced the first laser-assisted oxygen jet cutting system, revolutionizing the way sheet metal was cut. By the 1970s, manufacturers globally adopted laser cutting systems for a wide range of applications, from cutting titanium for aerospace to slicing textiles.
Today, laser cutting services have advanced significantly. CO2 lasers, which couldn’t cut through metal in the 1970s, are now powerful enough to do so. Overall, laser cutting has become more affordable, efficient, precise, and versatile with new wavelength bands. This trend is expected to continue as technology progresses.
Laser Cutting Service Details
Laser cutters are often managed by precision programs. These programs, which guide the laser cutting process with minimal human intervention, receive their instructions from CNC systems that use CAD designs to provide machining details.
In general, laser cutting services go like this:
- Our precision program gathers the essential information needed for accurate laser machining.
- Technicians and the cutting machine direct laser beams onto the materials for modification.
- Both the workpiece and the beam can move to melt the workpiece in localized areas. We use CNC control to focus and direct the laser beam, sometimes combined with fiber optics or mirrors.
- Technicians often pair an “assist gas,” such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide, with laser cutting to prepare newly cut surfaces for painting or corrosion-resistant coating. For instance, CO2 laser cutting, a gas-assist laser cutting technique, is renowned as the most powerful wave laser in the world today.
Laser Cutting Design
Before starting the laser cutting process, we carefully plan our approach based on various factors relevant to your application. These factors include the material of the part, the required tolerances, the dimensions of the part, the preferred laser cutting system, and the position of the head or nozzle.
We can create custom laser-cut products by adjusting specific elements of the laser cutting machine. These adjustments include CNC programming inputs, cut speed, heat-affected zone (HAZ), and the type of assist gas used.
Machinery Used in Laser Cutting Services
To perform our services, laser cut part manufacturers use various main laser types. These include metal lasers, fiber lasers, Neodymium (Nd) lasers, Neodymium yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd: YAG) lasers, CO2 lasers, and high-powered lasers.
Metal lasers are lasers specifically designed by manufacturers to exclusively modify metal workpieces. Common metals that are often laser cut include titanium, stainless steel, carbon steel, mild steel, and scribing metals.
Fiber lasers utilize fiber optic lasers enhanced with rare earth elements like ytterbium, thulium, and erbium. These lasers are favored due to their low operating costs, minimal maintenance needs, and absence of moving parts.
Fiber lasers are a unique category of solid-state lasers, utilizing optical fibers as their gain medium. These fibers are composed of silica glass infused with rare earth elements. The distinctive property of the silica glass in these fibers is its ability to emit light, making it exceptionally suitable for various applications. The light is more compact and linear than any other laser, aiding in precise, focused tasks.
Fiber lasers are cost-effective, require minimal maintenance, have a smaller footprint, and are highly efficient. They are utilized in laser cutting, texturing, marking, and welding.
A specially-designed glass fiber harnesses energy from pump diodes for this purpose. Fiber lasers boast a lifespan of 25,000 working hours and can amplify intensities up to 100 times higher than CO2 lasers. These lasers achieve smaller focal lengths with a wavelength of 1.064 micrometers.
Fiber lasers find applications in a wide range of fields and are particularly effective for metal markings, engraving, and marking thermoplastics. Additionally, they perform well with non-metals, glass, wood, and plastic.
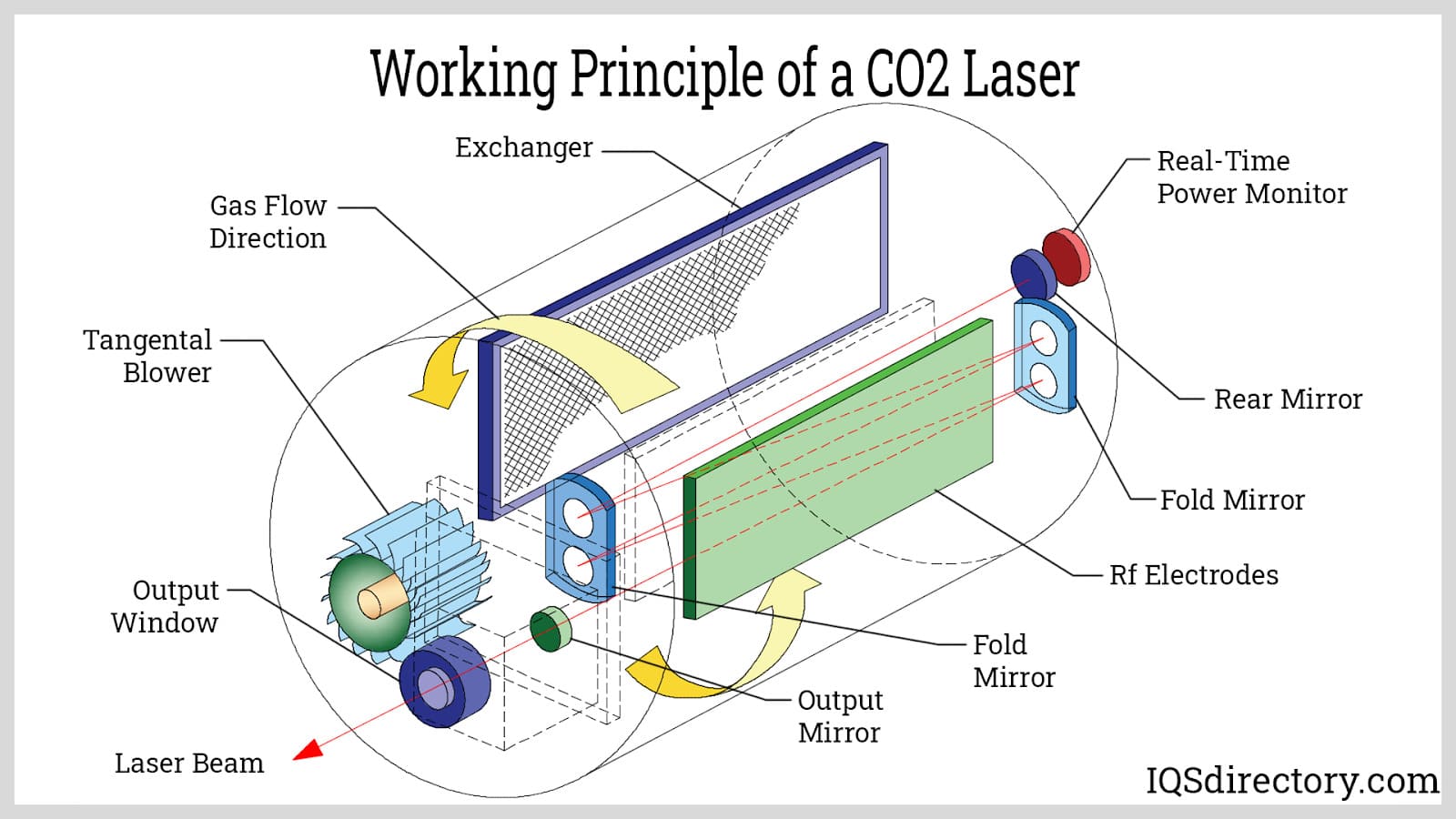
CO2 lasers are incredibly versatile, able to cut materials ranging from wood and stainless steel sheets to paper. These lasers are primarily chosen by manufacturers for industrial cutting, engraving, and boring tasks. There are several subtypes of CO2 lasers, including slab lasers, slow axial flow lasers, fast axial flow lasers, and transverse flow lasers.
This laser operates by channeling electricity through a gas-filled tube. This process generates a light beam within the tube, which is an invisible light falling within the far infrared range. The gasses utilized in CO2 lasers include carbon dioxide, helium, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
In this process, they use a tube with mirrors at both ends—one being fully reflective and the other partially reflective. A typical CO2 machine operates with a power range of 25-100 Watts and a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers. This laser excels in working with non-metallic materials but can also cut thin aluminum sheets and other non-ferrous metals. Increasing the oxygen content in this laser can enhance its power, though it becomes more challenging to manage.
CO2 lasers are widely utilized for cutting and engraving materials like wood, plastic, paper, leather, fabrics, wallpapers, and acrylic plastics. Additionally, these lasers find applications in food processing, such as preparing chestnuts and cheese.
Neodymium (Nd) lasers are a type of fiber laser. They excel in applications that demand high energy with low repetition, making them ideal for precision tasks. These lasers are commonly used in laser welding and are particularly effective with ceramic materials and scribing metals.
Neodymium yttrium-aluminum-garnet (Nd: YAG) lasers, a type of fiber laser, are very similar to Nd lasers. They excel in engraving and boring applications that require exceptionally high power. Additionally, they are suitable for laser welding.
These lasers use specialized crystals (Nd: YAG) or crystallized material (Nd YVO) as their medium:
Crystal laser cutting can be achieved using Nd YAG lasers, though Nd YVO lasers are more commonly employed for this purpose. These lasers boast high cutting power but come with a significant cost. They operate at a wavelength of 1.064 micrometers and have a lifespan ranging from 8,000 to 15,000 hours.
Nd YVO lasers boast high pump absorption, broader bandwidth, high refractive index, and low thermal conductivity. They find applications in various fields, including medical, military, and manufacturing settings. These lasers are effective for use with metals, non-metals, ceramics, and plastics.
High power lasers are specifically engineered to cut robust materials, such as stainless steels, mild steels, and scribing metals. These lasers can also serve multiple other purposes, making them highly versatile.
Semiconductor lasers, also known as laser diodes, feature a PN-junction.
The PN-junction of diodes is covered with a layer that enables spontaneous emission. This polished layer amplifies the emitted photons, transforming electric current into laser energy. We commonly find these in barcode readers, laser pointers, laser printers, and laser scanners.
Dye lasers are liquid lasers that utilize organic dye in liquid form as their gain medium.
Dye lasers offer a broad spectrum of wavelengths that can be adjusted at any point during their use. We utilize these versatile lasers for applications such as spectroscopy, birthmark removal, laser medicine, and isotope isolation.
Solid-state lasers operate by utilizing solids like crystal or glass combined with rare elements.
These elements include neodymium, chromium, erbium, and ytterbium. The ruby laser was the first solid-state laser ever constructed. These lasers are utilized in various applications such as tattoo making, hair removal, tissue ablation, and kidney stone removal.
Gas lasers generate light by channeling an electric current through a gas.
This process is called population inversion. We typically use gasses like CO2, krypton, helium-neon, and argon for these applications. These lasers find their place in holography, spectroscopy, material processing, barcode scanning, and laser surgery.
Laser Cutting Variations and Similar Processes
Variations on laser cutting include laser drilling, waterjet cutting, laser engraving, fusion cutting, thermal stress cracking, and laser welding.
Laser drilling is a technique used to create precise holes, whether for decorative or functional purposes. By employing laser beams, service providers achieve holes with tight exact tolerances, ensuring high accuracy and quality.
Waterjet cutting replaces lasers with highly pressurized water. This method allows manufacturers to save money, resources, and energy. However, it isn’t suitable for all materials. Manufacturers can only use it on specific types, as it won’t work on hard materials and is likely to break delicate ones like glass.
Fusion cutting, or melt and blow cutting, operates by using pressurized gas to expel molten material from the cutting zone. This method eliminates the need to elevate the material’s temperature, making it a favorite among manufacturers due to its low power consumption.
Thermal stress cracking offers an alternative to traditional cutting methods by utilizing localized surface heating to induce thermal expansion. This process is particularly effective with brittle materials, which are highly sensitive to thermal expansion. By directing a laser beam, manufacturers can control the cracking pattern precisely. This technique is especially well-suited for glass.
Laser welding, also known as laser beam welding, is a technique where laser cutters join large volumes of thermoplastics or metals. The machines used in this process emit focused, high-heat beams, creating deep, precise, and narrow welds. This method is especially useful in automotive manufacturing.
Laser engraving, or laser etching, allows us to precisely etch surfaces by vaporizing or fracturing them instead of melting them. This process is carried out with laser engraver machines, controlled by a combination of CNC technology, CAD programming, and human operators. In this method, a high-energy laser beam is used to locally irradiate the workpiece, resulting in permanent marking by marking, vaporizing, or changing the color of the surface material. Over the years, laser engraving has become an integral part of the industry, enabling us to create permanent markings, patterns, symbols, or writings on sheet material with high speed and precision. Laser engraving machines achieve this with the help of specialized tools designed for detailed carvings.
Laser engravers excel in precision due to the incredibly thin laser spot that targets a specific area. The engraver pinpoints the exact location to be engraved and directs a focused beam of light, altering its properties and appearance. This level of accuracy makes laser engravers indispensable across various industries. Whether it’s jewelry, medical kits, or wooden and plastic sheets, laser engraving can be applied to almost any material.
Laser engraving functions by vaporizing the material’s surface, creating fumes and etching permanent, deep marks onto it. Similar to an inkjet printer but employing lasers instead of ink, a laser engraving machine utilizes a high-powered laser to engrave a designated area.
They program the desired design, which is then sent to the laser engraving machine. After placing the material inside the machine, the laser beams start engraving it. The areas exposed to the lasers receive intense heat energy, sufficient to vaporize the surface.
Laser engraving is a precise technique that can handle various types of media. They use it for a wide range of applications due to its accuracy, consistency, and safety.
Laser engraving offers a high-speed, cost-effective solution. We use laser engravings for prototyping, whether we’re developing an app or creating a physical product.
They use laser engravings to personalize products by adding important information to them. Additionally, they use laser engravings to decorate various items.
There are three types of laser engravings. These are:
Cutting and Engraving
They use this cutting method to engrave patterns onto the surface material. The patterns are broken down into lines and then cut with a laser.
In this engraving process, they follow the same technique as laser cutting but focus on the material’s surface. First, they decompose the desired pattern and outline the lines. Lasers then cut these lines, bringing the pattern to life.
Concave Carving
This type is commonly used in two scenarios. The first involves a consistent cutting process across the surface, perfect for creating patterns of objects like animals or plants. The second method involves creating contrasting dark and light patterns, ideal for capturing finer details such as facial expressions.
To achieve concave engraving, they outline the surface material with the desired pattern. This process retains the material surrounding the pattern, and the same cutting force is uniformly applied to all parts.
Another method for creating concave engravings involves using varying light and dark patterns. The darker areas are cut or engraved more deeply, while the lighter areas are engraved less.
This outline pattern is designed for engraving animals, characters, and plants. The dark pattern, on the other hand, highlights details like facial expressions and specific features.
Convex/Toppan Engraving
In this type of engraving, the material surrounding the pattern is cut away, making it ideal for graphics, outlines, and text.
Convex engraving involves cutting the material uniformly around the pattern with consistent force at every point. It works well for text, graphic outlines, and similar designs. Both engraving methods rely on the movement of the laser head to remove the material.
Differences Between Laser Cutting and Engraving
Laser cutting and engraving are performed using the same machine, but they differ in their processes. Laser cutting involves a focused laser beam melting and cutting through a specific area, while laser engraving uses the beam to create marks by vaporizing the material into fumes, leaving permanent impressions on the surface.
The key distinction between these two processes lies in the lens of the laser machine. For engraving, a lens with a shorter focal length is used to achieve fine details on the material. In contrast, a longer focal length lens is employed for cutting, making it easier to slice through thicker edges.
Components of a Laser
- Energy Source
The role of the energy source is to inject light into the gain medium. This can vary depending on the type of laser, such as an electric discharge, laser diode, or flashlight.
- Gain Medium
The gain medium operates by emitting light across various wavelengths. It serves as the source of optical gain and is named according to the specific type of gain medium used.
- Resonator
Mirrors encircle the gain medium, with the resonator amplifying the optical gain by employing these mirrors.
Applications of Laser Engraving and Cutting
We use laser engraving to etch designs on awards and trophies, create barcodes on various materials, and add decorative elements to items, as well as for medical and electronic components. We use laser cutting in the automobile industry to create replicas and dies. In aerospace, it serves a crucial role in welding applications. The jewelry industry also benefits from laser cutting for crafting intricate pieces. Additionally, we employ laser cutting and engraving techniques to produce detailed wooden signboards.
Laser Cutting Benefits
There are numerous reasons to appreciate laser cutting. For one, it produces parts with virtually no edge deformation, roll-off, or edge factor, resulting in minimal burring on the cut edges. Additionally, laser cutting offers consistently faster turnaround times compared to other fabrication methods. This efficiency is partly due to the ease with which design changes can be implemented. The use of CNC machinery in laser cutting further enhances its benefits, reducing the need for numerous technicians and ensuring greater safety. Finally, laser cutting is incredibly versatile, offering a wide range of options while generating minimal waste.
Things to Consider Regarding Laser Cutting Services
Disadvantages
This popular cutting method comes with some drawbacks, primarily due to the high temperatures involved. For instance, the intense heat can cause narrow sections of the material to expand or warp. When oxygen is used as a gas assist, it can stress the cut edge, leading to distortion and oxidation, particularly in dense hole patterns. Lasers are also less effective on metals like aluminum and copper alloys, as these materials reflect light and handle heat differently. They are not suitable for non-metals such as glass or crystal. Furthermore, lasers require significant energy, which, along with limited material compatibility, makes the process more expensive. Additionally, lasers, especially infrared and ultraviolet ones, pose risks to eye safety.
Even with these limitations, laser cutting presents manufacturers with clear benefits compared to traditional methods like mechanical and thermal machining, EDM, arc welding, and flame cutting. The stability of motion systems guarantees exceptional control over laser beams and results in remarkably high-quality cuts. The precision of laser cutting surpasses all other techniques, offering slightly finer tolerances and narrower slicing widths than water jet cutting.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer
Should you choose to pursue laser cutting services, it’s essential to partner with a reputable provider. To help with this, we’ve compiled a list of top-rated, industry-leading laser cut parts manufacturers. Before diving into the list, we recommend preparing a detailed list of your requirements, questions, and concerns. Include information such as project descriptions, pattern requests, request volume, budget, timeline, preferred delivery methods, and any standard requirements.
Once you’ve put together your list of specifications, start exploring the laser cut service providers listed on this page. They’re nestled between the informational paragraphs, each with its own profile. As you review your options, keep your specifications list handy for easy comparison. Select three or four manufacturers you’d like to engage with in detail, then reach out to them individually. Pay attention to their attitude and responsiveness, as excellent customer service can be as crucial as pricing. After you’ve spoken with each, choose the one that seems to offer the best value. Then give them a call and kick off the process.




 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting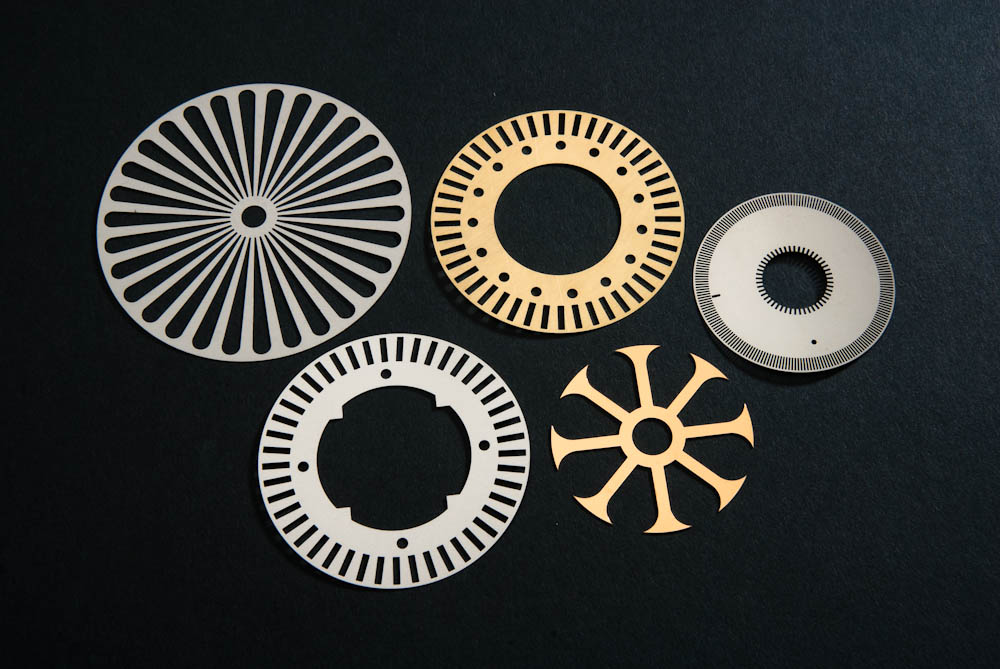 Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication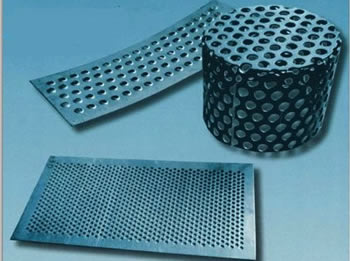 Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services